Table of Contents:
Rise of Biometric
Related Stories
Explore the rise of biometric payments and how your body is becoming your wallet. Learn about the biometric screening, advantages, use cases, security concerns, and future trends of biometric payment systems.
In the ever-evolving world of financial transactions, payment systems have undergone significant transformations, moving from tangible methods like cash to more convenient digital solutions. From the introduction of credit and debit cards to the rise of mobile payments, each advancement has made the act of purchasing goods and services more seamless. However, the next frontier in payments is not about cards or mobile phones but something far more personal—your body.
Enter biometric payments, a cutting-edge technology that uses the unique biological traits of individuals, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and even heartbeat patterns, as payment methods. This evolution is not only a leap forward in convenience but also a step toward enhancing the security and personalization of financial transactions. The prospect of paying for items simply by looking at a screen or scanning your fingerprint is no longer the stuff of science fiction. Instead, it is rapidly becoming a reality in our modern financial landscape.
This blog post will explore the concept of biometric payments, how they work, the benefits they offer, and their current and future applications. We will also delve into the privacy concerns and challenges that come with using biometric data, as well as examine the future potential of this transformative technology.
What Are Biometric Payments?
Biometric payments refer to a payment method that authenticates transactions using an individual’s unique biological or behavioral characteristics. In simpler terms, biometric payment systems leverage parts of your body—fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, and even voice or heartbeat signatures—to verify your identity and authorize payments.
Unlike traditional payment methods, which rely on physical tokens like credit cards or digital codes such as PIN numbers, biometric payments directly link your body to your wallet. This means that to make a payment, all you need is yourself—no cards, no devices, no passwords. But what are the specific forms of biometric authentication used in these systems? Let’s take a closer look at the most common methods.
Fingerprint Scanning

Fingerprint recognition is perhaps the most familiar biometric authentication method, already widely used in smartphones and banking apps. Each individual’s fingerprint is unique, and this technology maps the distinct ridges and patterns on your fingertips to verify your identity.
The advantage of fingerprint scanning lies in its speed and simplicity, making it an ideal choice for many biometric payment platforms.
Facial Recognition
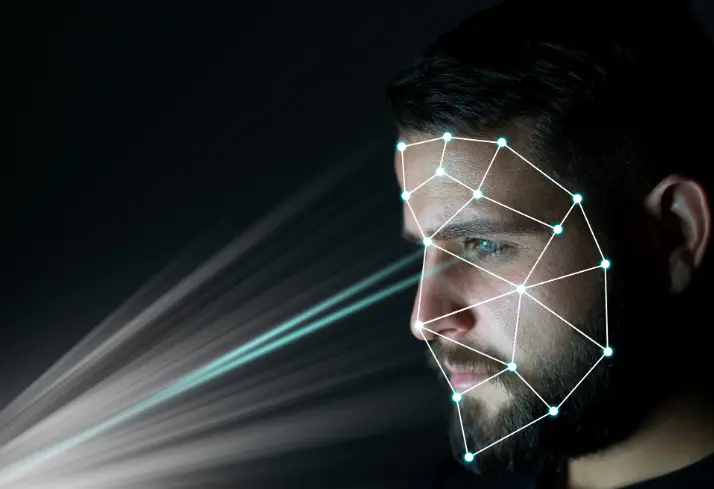

Facial recognition technology has gained popularity in recent years, largely due to its adoption by tech giants like Apple with Face ID. This method uses cameras and sensors to analyze the geometric features of a person’s face, including the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contour of the jawline.
This data is then converted into a mathematical model that can be used to authenticate payments.
Iris Scanning

Iris scanning offers an even higher level of security compared to fingerprints and facial recognition. The iris, a colored ring around the pupil, contains intricate patterns that are unique to each person.
By scanning the iris, biometric payment systems can accurately identify individuals and provide a robust security mechanism for authorizing transactions.
Voice Recognition

Voice recognition uses an individual’s unique vocal patterns for authentication. This method analyzes factors such as pitch, tone, and speech patterns to create a voice profile, which can then be used to verify a person’s identity during transactions.
Voice recognition is particularly useful for hands-free payment systems, such as those integrated into virtual assistants and smart speakers.
Heartbeat Signatures

An emerging form of biometric authentication is the use of a person’s heartbeat or cardiac signature. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, can measure the unique rhythm of an individual’s heart.
This data can be used as a biometric identifier to authenticate payments. Though still in its infancy, this method has the potential to revolutionize secure payments due to the high level of uniqueness and difficulty of replication associated with heartbeat patterns.
How Biometric Data is Processed Securely
Biometric payment systems typically employ a combination of hardware sensors and machine learning algorithms to capture and process biometric data. For example, a fingerprint scanner uses optical or capacitive sensors to map the fingerprint, while facial recognition systems use 3D mapping technology to create a digital profile of a face.
This data is then encrypted and stored either locally on the user’s device or in a secure cloud-based database. To ensure privacy and security, these systems often use decentralized storage models to minimize the risk of a large-scale data breach.
Advantages of Biometric Payments
Biometric payments offer a range of advantages over traditional payment methods, from enhanced security to improved convenience. Let’s dive into some of the key benefits that make biometric payments an attractive option for consumers and businesses alike.
Increased Security
One of the most significant advantages of biometric payments is the increased security they offer. Unlike passwords, PINs, or physical cards, which can be stolen, lost, or replicated, biometric data is much harder to forge or steal. Since your fingerprint, face, or heartbeat is unique to you, it adds a robust layer of protection against fraud. Additionally, biometric data is often encrypted and stored securely, ensuring that even if someone were to gain access to your biometric profile, they would still face multiple hurdles before committing fraud.
Reduced Fraud Risks
Biometric payments help to reduce the risk of identity theft and fraud. For example, if someone steals your credit card or phone, they can potentially use it to make unauthorized purchases. However, with biometric authentication, even if a device is stolen, the thief would not be able to access your funds without your fingerprint or facial scan.
Seamless User Experience
Biometric payments provide a more seamless user experience by eliminating the need for passwords, PINs, or physical wallets. The ability to authorize a transaction with a simple fingerprint scan or facial recognition speeds up the checkout process and reduces friction for consumers. This convenience is especially valuable in scenarios where speed is essential, such as contactless payments in public transportation or busy retail environments.
Faster Transactions
Biometric payments are designed to make transactions faster and more efficient. With no need to swipe a card or enter a PIN, the time it takes to complete a purchase is significantly reduced. This not only enhances the shopping experience for customers but also increases the throughput for businesses, especially in high-traffic areas like airports or event venues.
Financial Inclusion
Biometric payments have the potential to promote financial inclusion by providing access to banking and payment services for people who may not have traditional identification documents or access to banking infrastructure. In regions where people lack access to banks but have mobile phones, biometric payment systems can allow individuals to conduct transactions using just their fingerprint or voice. This opens up new opportunities for unbanked populations to participate in the global economy.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases

Biometric payments are no longer a futuristic concept—they are being implemented across various industries, from retail and banking to healthcare and public transportation. Here are some real-world examples of biometric payment systems in action:
Apple Pay and Face ID
Apple’s Face ID is one of the most prominent examples of biometric payments in the real world. With Face ID, users can authorize payments simply by looking at their iPhone or iPad. Apple Pay also integrates fingerprint scanning for older models using Touch ID.
The seamless integration of biometrics into Apple’s payment ecosystem has made it one of the most popular platforms for contactless payments.
Samsung Pay and Fingerprint Authentication
Samsung Pay uses fingerprint scanning as one of its primary authentication methods, allowing users to make payments securely with just a touch. Samsung’s technology is widely used in retail settings and online transactions, providing a fast and secure way for consumers to pay.
Amazon One
Amazon One is a biometric payment system that allows users to make purchases by scanning their palm. This contactless payment solution is currently being used in Amazon’s physical stores and other retail locations.
The system works by linking an individual’s palm signature to their payment account, allowing for a quick and secure checkout experience.
Biometric Payments in Retail
Biometric payment systems are being rolled out in retail environments across the globe. For example, in China, facial recognition is widely used in stores, allowing customers to pay simply by looking at a camera. Large retail chains are beginning to adopt similar technologies to offer a faster, more convenient checkout experience for their customers.
Banking and Financial Services
Banks are also adopting biometric payments as part of their security protocols. Many banks now allow customers to log into mobile banking apps using fingerprint or facial recognition instead of traditional passwords. Some financial institutions are experimenting with biometric ATMs, where users can withdraw cash by scanning their fingerprints or faces.
Healthcare and Insurance
Biometric payments are making their way into the healthcare sector as well, offering a secure method for patients to pay for medical services or access health insurance benefits. Biometric authentication can also be used to ensure the proper identification of patients, reducing the risk of medical fraud and identity theft.
Public Transportation
In cities like London and Tokyo, biometric payments are being tested in public transportation systems. Instead of using contactless cards or tickets, commuters can pay their fares by scanning their fingerprints or faces at the gates, speeding up the boarding process and improving convenience.
Privacy Concerns and Security Challenges

While biometric payments offer numerous benefits, they also raise important privacy and security concerns. As with any technology that handles sensitive data, there are risks associated with the collection, storage, and use of biometric information.
Data Breaches
One of the most significant concerns surrounding biometric payments is the risk of data breaches. Unlike passwords, biometric data cannot be changed or reset if it is compromised. This makes the security of biometric data storage critical. In recent years, there have been instances where hackers have successfully breached systems that store biometric information, leading to fears that biometric data could be misused or sold on the dark web.
Identity Theft
Although biometric authentication is generally considered more secure than traditional methods, it is not immune to identity theft. In some cases, biometric data can be spoofed or replicated using advanced technology, such as 3D-printed fingerprints or facial masks. This presents a new challenge for biometric payment systems: how to ensure that the biometric data being used is authentic and not a forgery.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Storage
The way biometric data is stored also presents privacy challenges. Centralized databases that store large amounts of biometric information can become attractive targets for hackers. To mitigate this risk, some companies are exploring decentralized storage solutions, where biometric data is stored locally on a user’s device rather than in a central database. This reduces the risk of a large-scale data breach but also presents its own set of challenges, such as how to ensure secure data transfer during transactions.
Regulatory Landscape
Governments and regulatory bodies are starting to take notice of the privacy and security risks associated with biometric payments. In some regions, regulations are being introduced to govern the use of biometric data, requiring companies to obtain explicit consent from users and implement stringent security measures to protect sensitive information. However, there is still much work to be done in creating a comprehensive regulatory framework that addresses the unique challenges posed by biometric payments.
The Future of Biometric Payments

The future of biometric payments is promising, with new innovations on the horizon that could further enhance the security and convenience of these systems. Here are some of the emerging trends and technologies that are likely to shape the future of biometric payments.
Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics is an emerging field that uses an individual’s behavior, such as walking patterns, typing speed, or hand movements, as a form of authentication. Unlike physical biometrics, which are based on fixed biological traits, behavioral biometrics analyze how a person behaves to verify their identity. This method can provide an additional layer of security, as it is more difficult to replicate someone’s behavior than their physical characteristics.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing a crucial role in improving the accuracy and security of biometric systems. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of biometric data to identify patterns and anomalies, making it easier to detect fraudulent activity. AI can also help enhance the user experience by making biometric systems more responsive and efficient.
Multimodal Biometrics
Multimodal biometrics refers to the use of multiple biometric data points for authentication, such as combining fingerprint and facial recognition or voice and iris scanning. By using more than one biometric identifier, multimodal systems can provide a higher level of security and reduce the likelihood of fraud. This approach is already being tested in high-security environments and could become more widespread in the future.
Global Commerce and Digital Wallets
As biometric payments continue to evolve, they are likely to play a significant role in the future of global commerce. Digital wallets that rely on biometric authentication could become the standard for international transactions, allowing users to make payments across borders with ease. This could help streamline global commerce and reduce the reliance on traditional banking infrastructure.
Conclusion
Biometric payments represent a significant leap forward in the evolution of payment systems, offering a more secure, convenient, and personalized way to conduct financial transactions. From fingerprint scans to facial recognition and even heartbeat signatures, biometric authentication is quickly becoming the preferred method for verifying identity and authorizing payments.
However, as with any emerging technology, biometric payments also come with their own set of challenges, particularly in the areas of privacy and security. It is essential for companies and regulators to work together to address these concerns and ensure that biometric data is handled responsibly.
External References
Biometric Payment Systems Explained
An article discussing the various types of biometric payment systems, how they work, and their benefits.
How Biometrics Are Transforming Payment Systems
A detailed overview of how biometric authentication is being implemented in payment systems worldwide.
Apple Pay: Secure Payments Using Biometrics
A case study on how Apple Pay utilizes biometric technology (Face ID and Touch ID) for secure payments.
The Role of Biometric Data in Financial Services
Insights on the use of biometric data in the financial sector, covering security challenges and regulations.
Amazon One: Palm Recognition for Payments
An article explaining how Amazon One uses palm recognition as a contactless payment method in retail.